Heating infrastructure management
DH.GIS is a source of data to plan network operations. It supports the maintenance of the network and its elements by helping to plan inspections, repairs, and reconstructions. It fully supports key processes at heating companies.
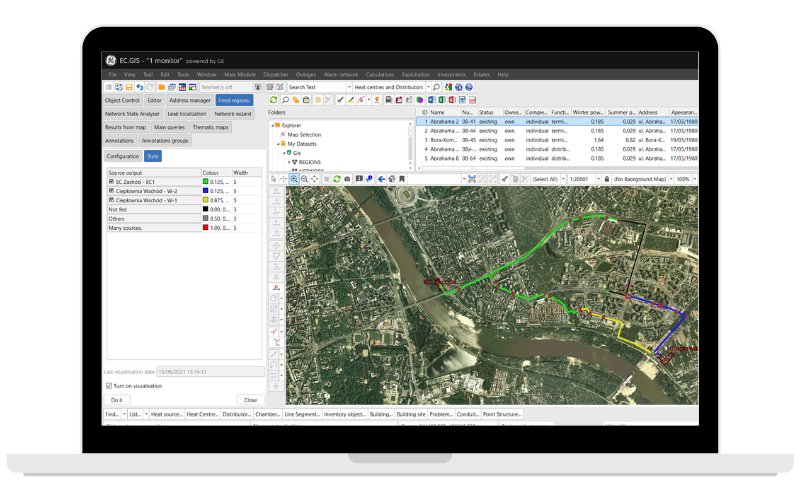
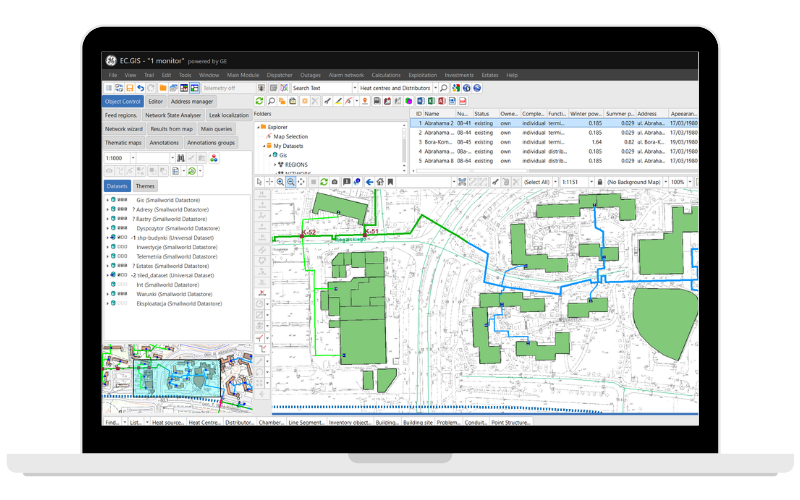
The main component of the solution is DH.GIS Main Module that includes a full data model conforming to the European standards. It allows you to create an asset inventory and topological model of the heating network. It’s based on a highly scalable and efficient Smallworld Core spatial database working in short and long transactions. GIS solutions based on the Smallworld system are currently implemented in over 350 energy companies around the world. DH.GIS is used in nearly 70 cities in Poland and 4 large cities in Ukraine.
The Dispatcher module supports dispatcher operations and provides tools for registering changes in shut-off valve status (open/close). Automated devices may be a part of the telemetry system and can be automatically registered in DH.GIS and displayed on a map. The system determines and displays current supply ranges for each source at any given time. It includes the areas and substations that aren’t supplied due to shutting off a part of the network.
DH.GIS Operations supports routine network maintenance activities such as:
– Periodic inspections of the network objects and registering their technical condition. This supports technical condition analyses of all the assets and discovering objects needing repairs.
– The node manager receives a document about substation operations and an option to register node incidents, particularly failures declared by the users.
The Outage Management module supports the whole process from identifying outage locations and affected customers, to connection analysis and restoring network stability.
This module supports the procedures for connecting new customers to the district heating network. It supports alphanumeric (descriptive), geometric (location) data and photographs, and related documents (e.g. legal status, local plans, agreements, etc.). DH.GIS stores the technical data and the exact location of the district heating infrastructure components, so it can analyze the potential increase in power demand after the updated network layout and hydraulic and thermodynamic calculations have been made.
This module enables planning investment activities in detail, such as network extension or reconstruction, and new customer connections. New parts of the network can be displayed on a map and analyzed in terms of their influence on the network with hydraulic and thermodynamic calculations. Several reports can be generated, including bill of materials, estimated cost of the investment over time, cost schedule, as well as simple ROI analysis that takes into account the investment cost, operations cost, and energy sale schedule.
The Real Assets module helps to manage assets located along with the network. It supports managing the lifecycle of the claim cases, compensation cases, cost analyses, and real asset easement.
This module allows you to load, store, and manage geodetic data from external sources. It includes many tools for building an initial geospatial database and allows users to analyze databases and reveal differences between them.
This module is used to maintain an alarm network along heating pipes in both a simplified and detailed way. Additionally, it provides an option for visualizing detector measurements.
The Calculations module is capable of performing complex hydraulic and thermodynamic calculations of the network. It helps to detect flows and pressure loss for end nodes in heating and water supply networks.
A data integration platform for processing, validating, and automated transferring of data. Supports maintaining an up-to-date database. The information collected during fieldwork can be automatically moved to DH.GIS simplifying the identification of areas for expansion.
This module displays layers directly from external sources, such as geodetic web services. The following data standards are supported: Google Maps, Open Street Map, WMTS, WMS, and WFS.
A Field Service Management system that supports planning optimal schedules and efficient fieldwork. Easily integrates with DH.GIS. The dispatcher and fieldworker apps make it easier to communicate and complete tasks.
An app that automatically categorizes documents and describes them by their issue date and location. It creates a spatial database and allows the user to easily access documents and display them on a map.
The DH.GIS system with related apps is used to maintain, develop, and build heating networks in 74 cities.
Heating networks modeled in Globema’s DH.GIS serve around 4,5 million consumers.
Globema has over 20 years of experience in creating and implementing specialized IT solutions for heating operators.
Globema acts as the Authorized Partner and the Value Added Reseller of GE Energy Smallworld GIS software in several European countries. GE also acts as Globema worldwide reseller of Globema’s telecommunication modules (PRM, ONA, RNI, DCM, CATV Design). The cooperation covers Smallworld software development & implementation as well as consulting & maintenance services. Since 1997, Globema has conducted hundreds of smaller and larger software delivery, development, and implementation projects for customers from over 30 countries.
GE’s software manages 40% of global electricity. It is designed to help utilities and telecommunication companies to better operate, analyze and optimize their operations. Applications based on the GE Smallworld platform are used by over 700 utility service providers (energy, heating, gas & oil, water) across 40 countries worldwide.